Base64 encoder
Created on 2 October, 2025 • Converter Tools • 70 views • 2 minutes read
Learn what a Base64 encoder is, how it works, and why it’s widely used in web development, email attachments, and data transfer. Understand the benefits, limitations, and common uses of Base64 encoding in a simple guide.
Base64 Encoder: Everything You Need to KnowIn today’s digital world, data is constantly being transferred between systems, applications, and networks. To ensure this process is smooth and reliable, different encoding techniques are used. One of the most popular methods is Base64 encoding. A Base64 encoder plays a crucial role in representing binary data in a text-friendly format that can be safely transmitted across platforms.
What is Base64 Encoding?
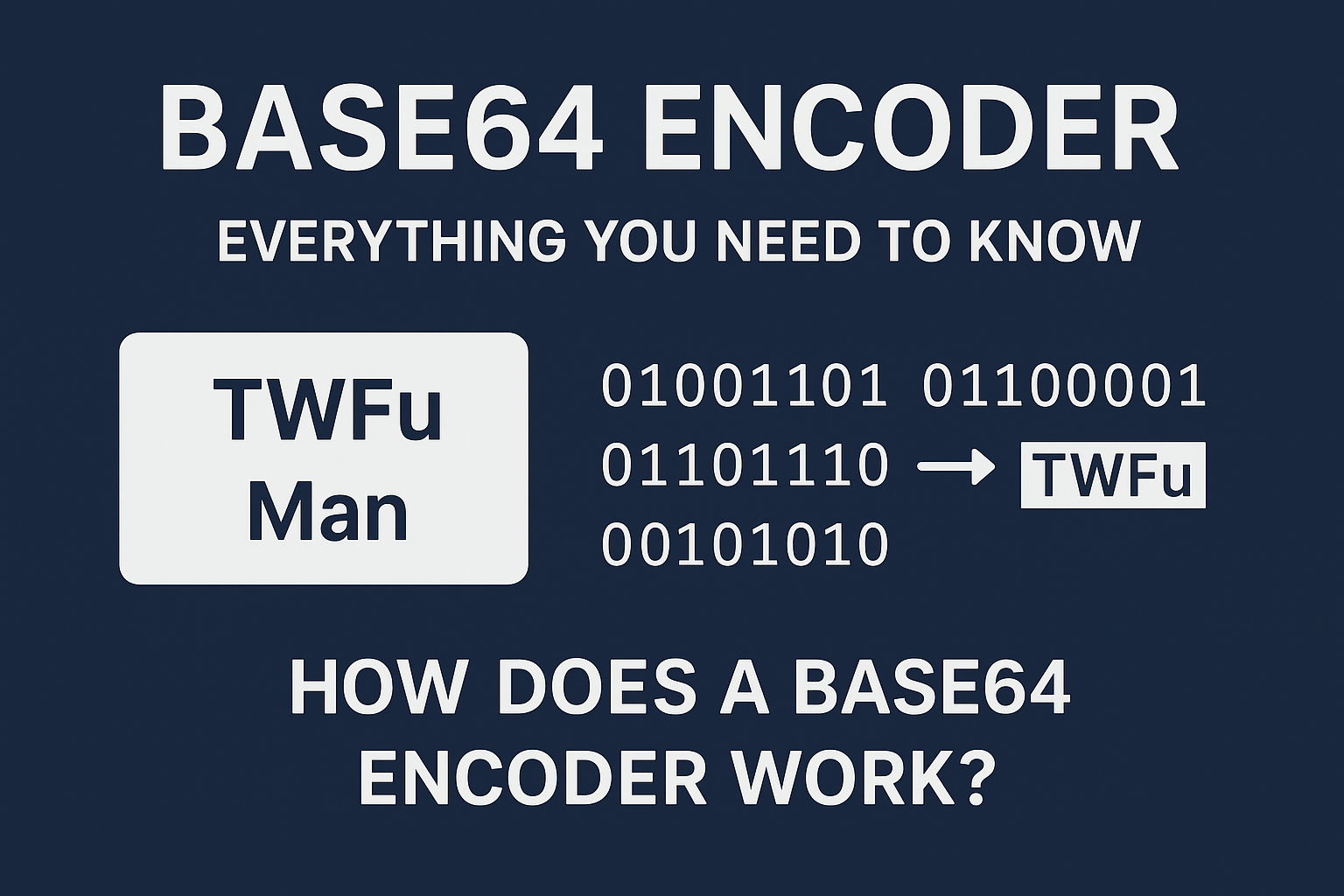
Base64 is a technique for converting binary data into a plain text format using a set of 64 ASCII characters. These characters include uppercase letters (A–Z), lowercase letters (a–z), numbers (0–9), and two special symbols (+ and /). In some cases, the equal sign (=) is added at the end as padding.
The main purpose of Base64 encoding is to make binary data readable by systems that only accept text-based formats. This makes it an essential tool in fields like email, data storage, and web development.
How Does a Base64 Encoder Work?
A Base64 encoder transforms raw binary data into a sequence of readable characters. It works by dividing the data into smaller chunks, converting them into numerical values, and mapping them to characters from the Base64 index table.
For example, when a text string or file is passed through a Base64 encoder, it becomes a long sequence of letters, numbers, and symbols. This transformation ensures that the data remains intact even when transferred through systems that do not support binary formats.
Why Use Base64 Encoding?
1. Data Transmission
Many protocols and applications support only text-based data. Base64 encoding allows binary files like documents, images, or audio to be transmitted safely without being altered or corrupted.
2. Embedding Media in Web Pages
Web developers often use Base64 encoding to embed small images directly inside HTML or CSS files. This reduces the need for separate image requests and can improve website performance for small graphical elements.
3. Email Attachments
Email systems use Base64 encoding through MIME (Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions) to send attachments such as PDFs, images, and documents in a text-compatible format.
4. Data Obfuscation
Although not a security measure, Base64 provides basic obfuscation. It makes raw binary data less readable to humans, which can be useful in hiding sensitive but non-critical information.
Limitations of Base64 Encoding
While Base64 encoding is widely used, it has some drawbacks:
Increased Data Size: Encoded data becomes about 33% larger than the original binary file.
Not Secure: Base64 is not encryption and should not be used to protect sensitive information.
Performance Issues: Using Base64 for large files, especially images, can slow down web applications.
Common Uses of Base64 Encoders
Base64 encoders are commonly used in:
Email systems for attachment encoding
Web development for embedding small media files
APIs and data transfer protocols
Text-based storage of binary data
With online Base64 encoder tools and built-in support in many programming languages, using Base64 is straightforward and accessible to anyone working with data.
Conclusion
A Base64 encoder is an essential tool in data communication and web technologies. It ensures that binary data can be safely transmitted in a text-friendly format across systems, emails, and web applications. However, it is important to remember that Base64 encoding is not encryption and should not be relied upon for security.
By understanding the strengths and limitations of Base64 encoding, developers, businesses, and everyday users can make smarter decisions when handling data.
Popular posts
-
Barcode readerMisc Tools • 160 views
-
Color pickerMisc Tools • 122 views
-
Exif readerMisc Tools • 117 views
-
SHA-256 generatorGenerator tools • 93 views
-
Ip LookupChecker Tools • 90 views