SHA-1 generator
Created on 4 October, 2025 • Generator tools • 74 views • 2 minutes read
"Learn everything about the SHA-1 generator, how it works, its applications, and why it’s no longer secure for modern cryptography. Understand file verification, password hashing, and better alternatives like SHA-256."
SHA-1 Generator: A Complete GuideIn the world of data security and cryptography, hashing algorithms play a significant role in ensuring integrity and authenticity. One of the most widely known hashing algorithms is SHA-1 (Secure Hash Algorithm 1). Although it has been largely replaced by more secure algorithms like SHA-256, the SHA-1 generator is still used in certain legacy systems, file verification, and educational purposes. In this article, we will explore what a SHA-1 generator is, how it works, and its common use cases.
What is a SHA-1 Generator?
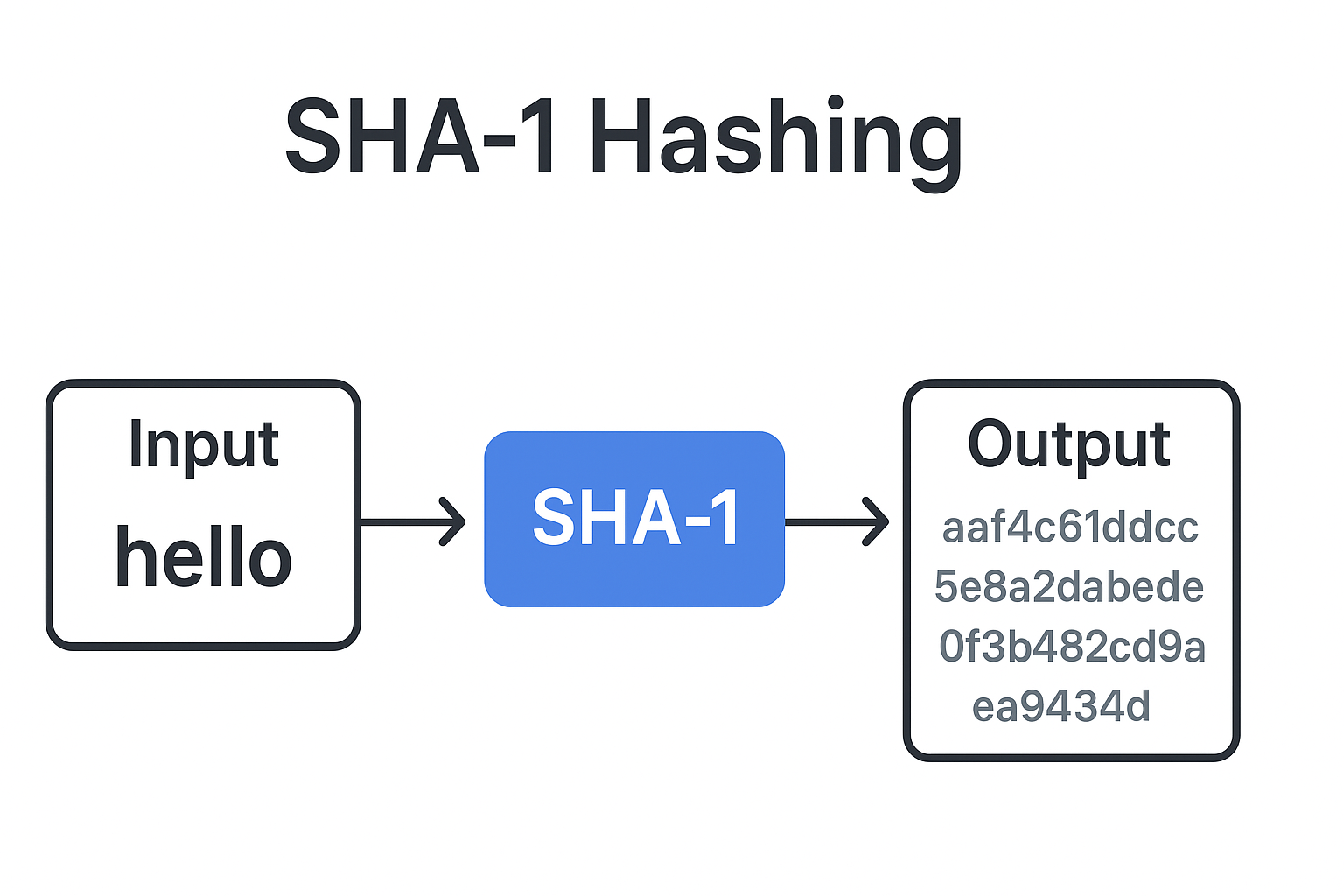
A SHA-1 generator is a tool or algorithm that takes an input—such as text, files, or passwords—and converts it into a 160-bit hash value (40-character hexadecimal string). This value is unique to the input data, meaning that even a tiny change in the input will result in a completely different hash output.
For example:
Input: hello
SHA-1 Hash: aaf4c61ddcc5e8a2dabede0f3b482cd9aea9434d
This one-way function ensures that the hash cannot be reversed to reveal the original input, which makes it useful in security applications.
How Does SHA-1 Work?
SHA-1 works by processing data in 512-bit blocks and applying a series of bitwise operations, modular additions, and logical functions to produce the final 160-bit hash. The process includes:
Pre-processing – Padding the input message to fit block sizes.
Message parsing – Breaking input into 512-bit chunks.
Processing – Applying 80 rounds of mathematical operations.
Final hash output – Producing a 160-bit unique hash string.
This makes SHA-1 a deterministic algorithm: the same input will always produce the same hash.
Applications of SHA-1 Generator
Even though SHA-1 is considered weak today, it has been widely used for years. Some of its common applications include:
1. File Integrity Verification
When downloading software or updates, websites often provide a SHA-1 checksum. Users can generate the SHA-1 hash of their downloaded file and compare it to ensure the file has not been tampered with.
2. Password Hashing (Legacy Systems)
Older systems used SHA-1 to store password hashes instead of plain text. However, modern systems now use bcrypt, SHA-256, or Argon2 for stronger security.
3. Digital Signatures & Certificates
SHA-1 was used in SSL/TLS certificates and digital signatures, but due to vulnerabilities, it is no longer recommended in cryptographic security.
4. Data Deduplication
Some systems use SHA-1 hashes to quickly identify duplicate files by comparing their hash values.
Is SHA-1 Still Secure?
While SHA-1 served as a reliable hashing algorithm for decades, it has been proven vulnerable to collision attacks (where two different inputs produce the same hash). In 2017, Google demonstrated the first practical SHA-1 collision attack called SHAttered.
Because of these vulnerabilities:
Major browsers stopped supporting SHA-1 certificates.
Security experts recommend migrating to SHA-256 or SHA-3.
Conclusion
A SHA-1 generator is a tool that converts input into a fixed 160-bit hash, ensuring data integrity and uniqueness. While it is still used in file verification and legacy systems, it is no longer recommended for modern cryptographic applications due to its vulnerabilities. For secure hashing needs, developers should consider SHA-256, SHA-512, or more advanced algorithms.
By understanding how a SHA-1 generator works and its limitations, you can make informed decisions about when and how to use it.
Popular posts
-
Barcode readerMisc Tools • 160 views
-
Color pickerMisc Tools • 122 views
-
Exif readerMisc Tools • 117 views
-
SHA-256 generatorGenerator tools • 93 views
-
Ip LookupChecker Tools • 90 views